Advances in Pharmaceutical Excipients Supporting Next-Gen Therapies
Pharmaceutical excipients, once deemed inert carriers, have evolved into active enablers that significantly influence drug stability, delivery, and bioavailability. As next-generation therapies—such as mRNA treatments, antibody–drug conjugates, and cell-based products—gain clinical prominence, the demand for novel excipients tailored to complex formulations surges across the global pharmaceutical sector.
The Role of Novel Excipients in Next-Gen Drug Delivery
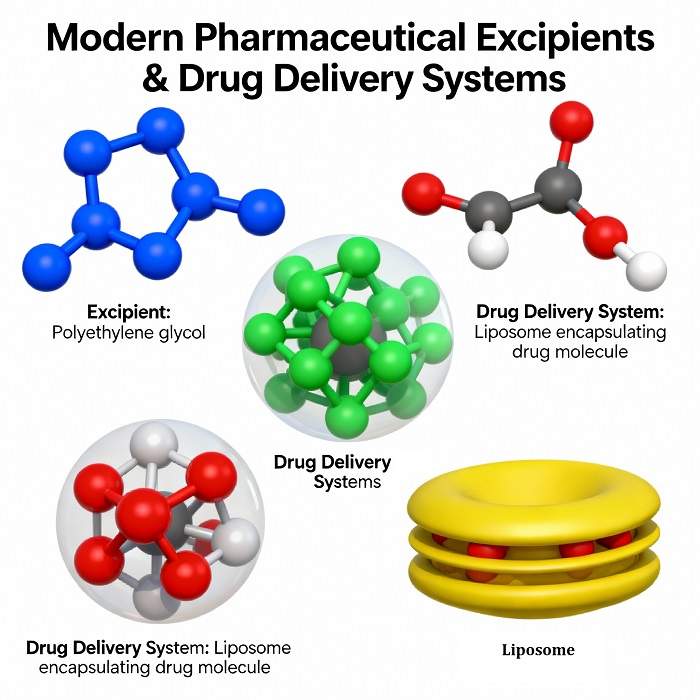
In the realm of advanced therapeutics, standard excipients often fall short in addressing unique solubility and stability challenges. Consequently, researchers have pioneered pharmaceutical excipients for new therapies, leveraging materials science breakthroughs to develop lipid nanoparticles, stimuli-responsive polymers, and prodrug-enhancing carriers that optimize targeted delivery.
Lipid-Based Systems and mRNA Therapeutics
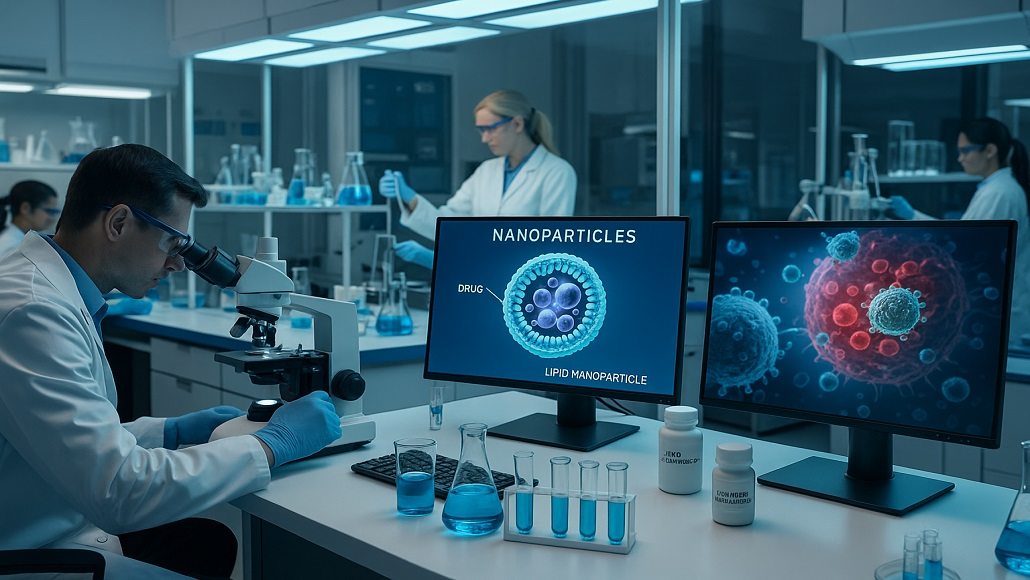
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as the cornerstone of mRNA delivery, offering protective encapsulation and controlled release profiles. By fine-tuning ionizable lipids, cholesterol ratios, and surface modifications, developers achieve efficient endosomal escape and enhanced cellular uptake—critical for ensuring robust expression in therapeutic applications.
Stimuli-Responsive Polymers for Controlled Release
Stimuli-responsive excipients, designed to react to pH shifts, temperature changes, or enzymatic triggers, are transforming controlled-release paradigms. For instance, pH-sensitive polymers can disassemble within the acidic tumor microenvironment, enabling targeted anticancer payload delivery while minimizing systemic exposure.
Collaboration Between Excipients Innovators and Pharma
Driving these advances is a burgeoning collaboration between excipient suppliers and biopharma firms. Joint partnerships facilitate co-development of bespoke excipient platforms, ensuring compatibility with proprietary therapeutic modalities and expediting regulatory approval processes.
Regulatory Considerations and Safety Profiles
Given their active roles, novel excipients undergo rigorous regulatory scrutiny. Agencies now require comprehensive biocompatibility and degradation studies to assess long-term safety. As regulatory frameworks adapt, excipient innovators must maintain transparent documentation to support accelerated pathways for breakthrough therapies.
Conclusion
The landscape of pharmaceutical excipients is rapidly expanding, driven by the complex demands of next-generation therapies. Through innovative materials and strategic collaborations, excipients now play pivotal roles in ensuring stability, targeted delivery, and patient safety. As the industry embraces these advances, the synergy between excipient science and therapeutic innovation will continue to propel drug development into new frontiers.