Middle East Pharma Hubs: Building Global-Standard Manufacturing Ecosystems
The pharmaceutical landscape across the Middle East is undergoing a remarkable transformation. What was once a region heavily dependent on pharmaceutical imports is rapidly evolving into a constellation of world-class manufacturing hubs capable of serving both regional and global markets. This strategic shift, driven by visionary government initiatives, substantial capital investments, and partnerships with multinational pharmaceutical companies, positions the Middle East as an emerging powerhouse in global pharmaceutical manufacturing. The implications extend far beyond economic diversification, touching on healthcare security, technological advancement, and the region’s broader ambitions to become a knowledge-based economy.
The scale of this transformation is evident in market projections and investment commitments. The Middle East pharmaceutical market, valued at 54.28 billion dollars in 2024, is projected to reach 78.30 billion dollars by 2033, representing steady growth driven by increasing healthcare expenditure, rising chronic disease prevalence, and expanding local manufacturing capabilities. Countries across the region have committed billions of dollars to pharmaceutical infrastructure development, from state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities to research centers focused on biopharmaceutical innovation. This investment wave creates opportunities for pharmaceutical companies, equipment suppliers, and life sciences professionals while fundamentally reshaping regional healthcare systems.
Strategic Government Initiatives Driving Growth
Saudi Arabia’s pharmaceutical transformation exemplifies the region’s ambitious approach to building manufacturing capabilities. The Kingdom’s Vision 2030 economic diversification strategy identifies pharmaceuticals as a strategic priority, targeting local production of 40 percent of pharmaceutical consumption. This goal drives multiple coordinated initiatives including the Biopharma Valley project near Riyadh, a 2.5 billion dollar investment creating a world-class biopharmaceutical cluster. This integrated development combines manufacturing facilities, research laboratories, and regulatory infrastructure designed to international standards, attracting both domestic startups and multinational pharmaceutical companies seeking Middle East presence.
The Saudi Food and Drug Authority has implemented fast-track approval pathways specifically for biosimilars and innovative biologics, harmonizing regulatory standards with those of the European Medicines Agency and Food and Drug Administration. This regulatory modernization reduces approval timelines while maintaining rigorous quality standards, making Saudi Arabia an attractive market for pharmaceutical innovation. The combination of market access incentives, manufacturing support programs, and streamlined regulatory pathways creates a comprehensive ecosystem that addresses multiple barriers traditionally facing pharmaceutical investment in emerging markets.
The United Arab Emirates has pursued a complementary but distinct strategy, leveraging its position as a regional logistics hub and emphasizing advanced manufacturing technologies. The Emirates Drug Establishment, formed in 2023, centralizes pharmaceutical regulation while implementing policies that encourage local manufacturing and clinical research. The UAE government aims to expand local drug production capacity by 40 percent annually, supporting this goal through infrastructure investments in specialized zones like Abu Dhabi’s Khalifa Industrial Zone. Over 35 pharmaceutical factories now operate across the UAE, a dramatic increase from just a handful a decade ago, producing more than 2,500 different medicines and pharmaceutical ingredients.
Egypt’s approach emphasizes its role as a manufacturing hub serving broader African and Middle Eastern markets. The establishment of a 120 million dollar pharmaceutical industrial complex in the Suez Canal Economic Zone illustrates this strategic positioning. The facility, spanning nearly 97,000 square meters, will produce active pharmaceutical ingredients and essential raw materials, addressing supply chain vulnerabilities while creating export opportunities. Egypt’s large population, established pharmaceutical industry, and strategic location between Europe, Asia, and Africa position it uniquely to serve as a regional manufacturing center, particularly for generic medicines where cost competitiveness is paramount.
Infrastructure Development and Manufacturing Capabilities
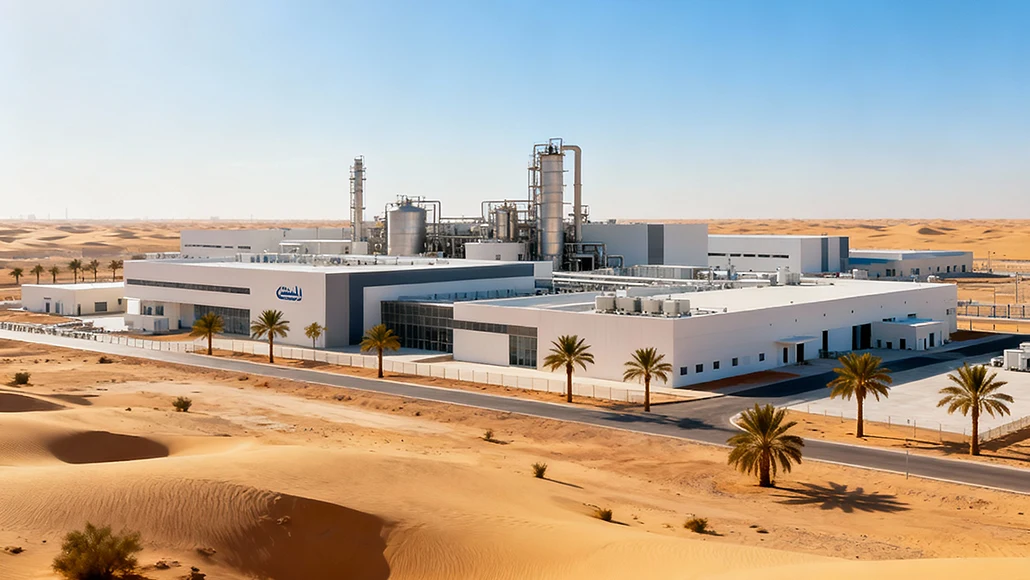
The physical infrastructure supporting pharmaceutical manufacturing across the Middle East increasingly matches global standards, with facilities designed and constructed to meet stringent regulatory requirements including Good Manufacturing Practice compliance and international quality certifications. New pharmaceutical plants incorporate advanced automation, continuous manufacturing technologies, and sophisticated quality control laboratories equipped with state-of-the-art analytical instruments. These investments ensure that Middle East-manufactured pharmaceuticals meet the same quality standards as products from traditional pharmaceutical manufacturing regions in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Specialized free zones and industrial parks provide pharmaceutical manufacturers with attractive operational environments. These developments offer streamlined customs procedures, tax incentives, modern utilities infrastructure, and proximity to international airports and seaports facilitating raw material imports and product exports. Dubai Science Park, Jebel Ali Free Zone in the UAE, and similar developments in Saudi Arabia and other Gulf Cooperation Council nations host regional headquarters of major pharmaceutical companies including Roche, Sanofi, Johnson & Johnson, and GlaxoSmithKline, demonstrating the appeal of these environments to global pharmaceutical industry leaders.
Cold chain infrastructure critical for biologics and vaccines has expanded dramatically, addressing a historical weakness in Middle Eastern pharmaceutical logistics. New temperature-controlled warehouses incorporate automated storage and retrieval systems, continuous monitoring, and backup power generation ensuring product integrity even during utility disruptions. Specialized logistics providers have established regional operations offering pharmaceutical-grade transportation with real-time tracking and quality documentation meeting international standards. This infrastructure enables the region to serve as a distribution hub for temperature-sensitive products destined for markets across the Middle East, Africa, and South Asia.
Analytical and quality control capabilities have kept pace with manufacturing expansion. Contract development and manufacturing organizations and pharmaceutical companies operating in the region have established sophisticated analytical laboratories capable of complex testing including biological assays, advanced chromatography, and stability studies. These capabilities enable complete in-region quality control, reducing dependence on sending samples to overseas laboratories and accelerating product release timelines. Some facilities have achieved recognition from major regulatory authorities, enabling them to perform testing accepted for regulatory submissions in highly regulated markets.
Technology Transfer and Knowledge Development
Pharmaceutical manufacturing expansion in the Middle East goes beyond brick-and-mortar infrastructure to encompass knowledge transfer and capability building. Multinational pharmaceutical companies partnering with regional entities typically include technology transfer components, training local scientists and engineers in manufacturing processes, quality systems, and regulatory compliance. These partnerships create valuable intellectual capital that supports long-term industry sustainability beyond any individual partnership or facility.
Universities across the region have expanded pharmaceutical sciences programs, recognizing industry demand for trained professionals. These academic programs increasingly emphasize practical skills including bioprocess engineering, pharmaceutical quality assurance, and regulatory affairs alongside traditional medicinal chemistry and pharmacology curricula. Some institutions have established research centers focused on regional health priorities including genetic disorders with high prevalence in Middle Eastern populations, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. These research efforts create opportunities for pharmaceutical innovation specifically addressing regional medical needs while building research capabilities that support industry development.
Regulatory capacity building represents a critical yet sometimes overlooked aspect of pharmaceutical ecosystem development. Effective pharmaceutical regulation requires specialized expertise in manufacturing inspection, clinical trial oversight, and post-market surveillance. Middle Eastern regulatory authorities have invested in training programs, international collaborations, and recruitment of experienced professionals to build these capabilities. Some regulatory agencies participate in international harmonization initiatives and mutual recognition arrangements, facilitating regulatory convergence that benefits both regional manufacturers and patients needing access to innovative medicines.
Public-private partnerships facilitate knowledge exchange while distributing development risks between government entities and private pharmaceutical companies. These collaborations take various forms including joint ventures, licensing agreements, and research partnerships, each contributing to overall ecosystem development. Governments provide financial support, infrastructure, and market access while pharmaceutical companies contribute technical expertise, established quality systems, and connections to global pharmaceutical networks. This collaborative model accelerates capability development beyond what either sector could achieve independently.
Manufacturing Focus Areas and Product Categories
Small molecule generic pharmaceuticals represent a natural initial focus for Middle Eastern manufacturing expansion, leveraging existing chemical manufacturing capabilities and addressing high-volume medical needs. Generic medicines for chronic conditions including hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia account for substantial pharmaceutical consumption across the region, creating robust demand for locally manufactured products. Manufacturing these medicines domestically reduces import dependence, creates employment, and develops foundational pharmaceutical capabilities that support progression to more sophisticated products.
Biosimilar manufacturing represents the next frontier, with several Middle Eastern facilities now producing or developing capacity for these complex biological medicines. Biosimilars offer substantial healthcare cost savings compared to originator biologics while requiring sophisticated manufacturing and quality control capabilities that elevate regional pharmaceutical industry capabilities. Collaborations between regional manufacturers and established biosimilar companies facilitate technology transfer while de-risking these complex development programs. The growing regional biosimilar manufacturing capability positions the Middle East to supply both domestic markets and export opportunities as biosimilar adoption accelerates globally.
Vaccine manufacturing has gained particular emphasis following COVID-19 pandemic experiences that highlighted vulnerabilities in vaccine supply chains. Several Middle Eastern countries have announced major vaccine manufacturing investments, including facilities capable of producing both traditional vaccines and newer platforms including mRNA vaccines. A 500 million Saudi Riyal investment in a vaccine manufacturing facility in Saudi Arabia exemplifies this commitment, aiming to achieve vaccine self-sufficiency while creating export capacity. These facilities will address regional vaccine needs while potentially serving as manufacturing sites for international vaccine programs targeting Middle Eastern and African markets.
Advanced therapy manufacturing including cell and gene therapies represents an aspirational but achievable goal for leading Middle Eastern pharmaceutical hubs. While this represents the most technically demanding pharmaceutical manufacturing category, some regional facilities are developing capabilities in this area through partnerships with specialized cell therapy companies. The high value of these therapies justifies the substantial investments required, while manufacturing complexity creates competitive moats protecting these capabilities once established. Success in advanced therapy manufacturing would position select Middle Eastern facilities at the technological frontier of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Regulatory Harmonization and International Standards
Regulatory frameworks across the Middle East continue evolving toward international harmonization, facilitating both regional trade and recognition of Middle East-manufactured products in global markets. Gulf Cooperation Council initiatives work toward unified pharmaceutical registration requirements, streamlining market access across member states while maintaining stringent quality standards. These harmonization efforts reduce duplicative regulatory requirements that historically impeded efficient pharmaceutical commerce across the region, creating a more attractive market for pharmaceutical innovation and investment.
International regulatory recognition represents a critical milestone for Middle Eastern pharmaceutical manufacturing aspirations. Several regional regulatory authorities have established inspection agreements and mutual recognition arrangements with major international regulatory bodies, enabling products approved in the Middle East to enter other markets more easily. Conversely, these arrangements facilitate access to innovative medicines developed elsewhere, benefiting regional patients while demonstrating regulatory system maturity. Pharmaceutical companies manufacturing in the region increasingly pursue international certifications and regulatory approvals, positioning their products for global markets rather than solely regional consumption.
Clinical trial infrastructure development supports pharmaceutical innovation while providing regulatory authorities experience overseeing research activities. Several Middle Eastern countries have established clinical trial frameworks modeled on international standards, attracting pharmaceutical companies seeking to include regional patient populations in global development programs. These trials generate valuable clinical data while exposing regulatory reviewers to cutting-edge pharmaceutical development, building expertise that informs regulatory decision-making. Some regional institutions are developing particular expertise in trials for genetic disorders with high regional prevalence, carving out niches in global pharmaceutical development.
Pharmacovigilance systems for post-market safety surveillance continue maturing, employing modern information technology platforms for adverse event reporting and analysis. Robust pharmacovigilance represents a fundamental regulatory responsibility, ensuring ongoing monitoring of pharmaceutical safety after market approval. Regional regulatory authorities increasingly collaborate internationally on safety issues, participating in information sharing networks that enable rapid response to emerging safety signals. This participation in global pharmacovigilance networks both protects regional populations and demonstrates regulatory sophistication that builds confidence in Middle Eastern pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Economic Impact and Future Outlook
The economic benefits of pharmaceutical manufacturing development extend across multiple dimensions. Direct employment in pharmaceutical manufacturing, quality control, and research activities creates high-skilled jobs contributing to economic diversification goals. Indirect employment in supporting sectors including specialized construction, equipment supply, logistics, and professional services multiplies these direct impacts. The knowledge-intensive nature of pharmaceutical manufacturing aligns with regional aspirations to transition from resource-based to knowledge-based economies, making pharmaceutical sector development particularly strategically valuable.
Import substitution represents an immediate economic benefit, reducing pharmaceutical import bills while improving healthcare cost sustainability. Middle Eastern countries historically imported the majority of pharmaceutical consumption, creating vulnerability to supply disruptions and currency fluctuations affecting import costs. Local manufacturing addresses both concerns while retaining pharmaceutical spending within regional economies. As local manufacturing capabilities mature and product portfolios expand, import substitution benefits will compound, potentially reaching billions of dollars annually across the region.
Export potential creates opportunities to transform pharmaceutical manufacturing from import substitution to foreign exchange generation. The strategic geographic position of Middle Eastern countries between major markets in Europe, Asia, and Africa provides logistical advantages for pharmaceutical exports. Free trade agreements and preferential trade arrangements with various international partners facilitate market access. As manufacturing quality and regulatory recognition continue developing, Middle Eastern pharmaceutical exports could expand significantly, contributing to broader economic growth while establishing the region as a globally significant pharmaceutical manufacturing location.
The transformation of the Middle East into a globally competitive pharmaceutical manufacturing region represents one of the most ambitious industrial development initiatives currently underway worldwide. Success requires sustained commitment from governments, continued investment from pharmaceutical companies, ongoing capability development among regulatory authorities and educational institutions, and patience as complex manufacturing and quality systems mature. The progress achieved to date demonstrates feasibility, while remaining challenges highlight the magnitude of the transformation still required. As Middle Eastern pharmaceutical hubs continue developing, they will increasingly influence global pharmaceutical supply chains, contribute to medical innovation, and demonstrate the region’s capacity for knowledge-based economic development.