Researchers at UCC have developed a microneedle-based patch that results in increased vaccine-induced protection against malaria infection using lower doses of vaccine in pre-clinical testing. The lead researcher, Dr Anne Moore, heads to Silicon Valley next week to meet venture capitalists and leading technology companies with a view to commercialising the research.
The microneedle-based patch also overcomes one of the main problems with this type of vaccine which relates to overcoming pre-existing immunity to the vaccine. The scientists combined two vaccine technologies to determine if immunity could be further enhanced and the research suggests that using a microneedle patch would overcome the need to make and use multiple different vaccine types to induce protective immunity to some of the world’s biggest killers. This could have significant consequences on the costs and logistics of vaccination.
The work was carried out by researchers in the School of Pharmacy, Dept. of Pharmacology and the Tyndall National Institute, UCC, led by Dr Anne Moore in collaboration with colleagues at the Jenner Institute, University of Oxford and was published by Nature Publication Group in Scientific Reports and funded by Enterprise Ireland and Science Foundation Ireland. Dr Moore’s visit to Silicon Valley is being hosted by the Irish Technology Leadership Group (ITLG) as part of an SFI initiative for researchers to help them develop their entrepreneurial skills in the Get Started Venture Technology programme.
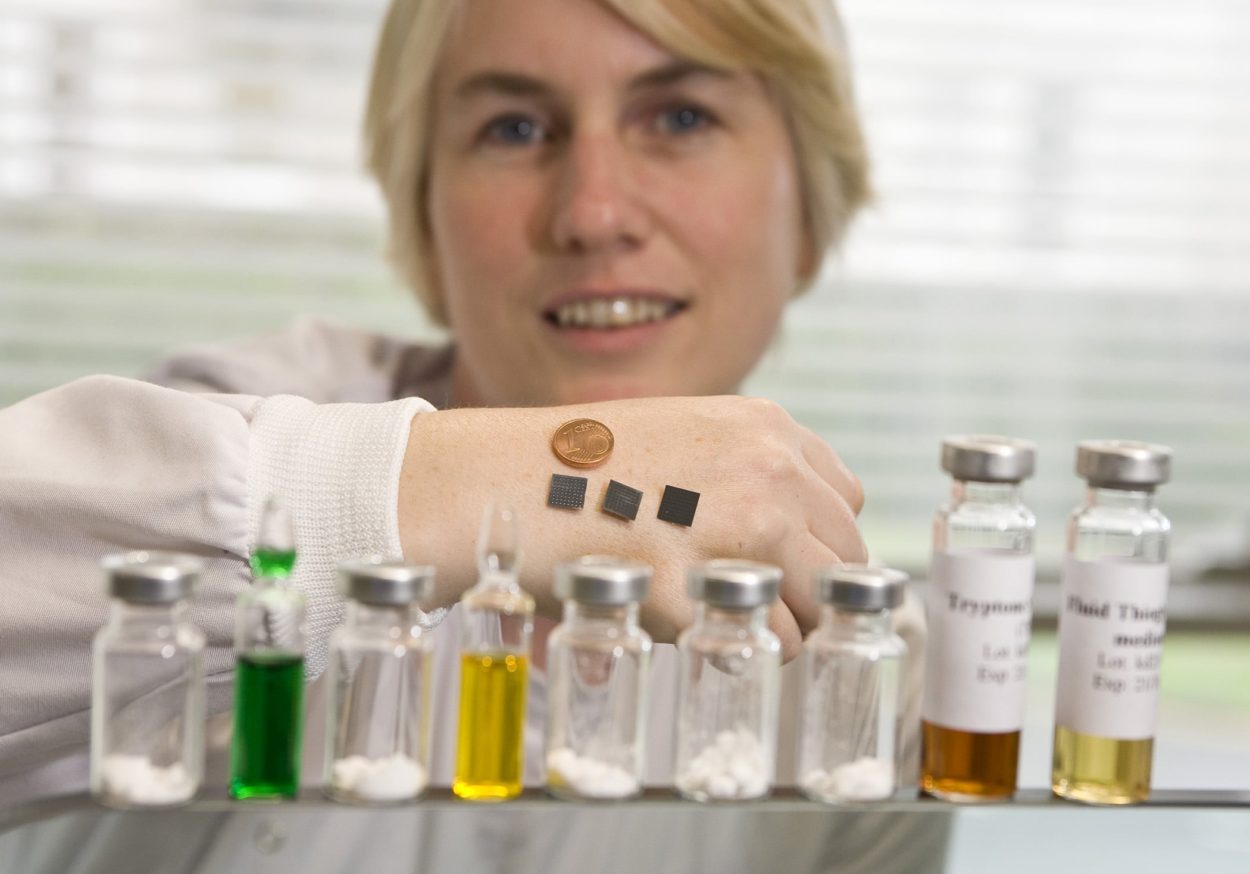
The skin patch has arrays of tiny silicon ‘microneedles’ that painlessly create temporary pores in the very outermost barrier layer of the skin, permitting the vaccine to flow into the skin, which is rich in cells of the immune system. The experimental vaccine was based on a live adenovirus. This virus is similar to those that can cause a common cold, but is engineered to be safer and to deliver a protein from the malaria-causing parasite, to the immune system.
Adenoviruses are one of the most potent vaccine platforms tested to date in humans and they are being developed to prevent or treat diseases such as malaria, HIV, influenza and Ebola and to combat other infectious diseases related to biodefence. An obstacle with this vaccine platform is that, although it is great for inducing high levels of immunity to the malaria or HIV protein of interest, a strong immune response to the adenovirus itself is also induced. This robust anti-adenovirus immunity prevents its repeated use as a vaccine as the immune system recognises the adenovirus and prevents it from delivering the malaria protein, so another vaccine type or adenovirus strain needs to be used in the booster immunization.
“What’s exciting from this work,” says Dr Moore “is that administration of this vaccine with the microneedle patch did not induce this strong anti-adenovirus immunity, even though very potent immunity to the malaria antigen is generated.” The team demonstrated that using the microneedle patch in the primary immunization does indeed permit repeated use of the same adenovirus vaccine and this immunization method induces potent and highly protective immune responses against malaria in pre-clinical studies.