The pharmaceutical manufacturing landscape is undergoing a profound structural shift, moving away from traditional batch-based testing and toward a more integrated, data-driven approach. At the heart of this transformation is process analytical technology in pharma, a system designed to design, analyze, and control manufacturing through timely measurements of critical quality and performance attributes. For decades, the industry relied on retrospective testing, where samples were taken at the end of a process and analyzed in a laboratory. While effective, this method was inherently slow and often resulted in significant waste if a batch was found to be non-compliant. Today, the integration of advanced sensors and real-time analytics is enabling a proactive manufacturing environment where quality is built into the process itself.
The Strategic Shift toward Quality by Design
The adoption of process analytical technology in pharma is deeply intertwined with the philosophy of Quality by Design (QbD). In a QbD framework, the manufacturing process is not merely a set of instructions but a deeply understood system where every variable is mapped and controlled. By utilizing PAT tools, manufacturers can identify the critical material attributes and process parameters that directly influence the final quality of the drug. This scientific understanding allows for the creation of a “design space” within which the process can operate with a high degree of certainty. When a process stays within this space, the quality of the product is guaranteed, significantly reducing the reliance on end-product testing and facilitating a more streamlined path to market.
Real-Time Monitoring and the End of Retrospective Testing
The primary advantage of implementing process analytical technology in pharma is the ability to achieve real-time monitoring of the production floor. Advanced spectroscopic tools, such as Near-Infrared (NIR) and Raman spectroscopy, allow for the non-destructive analysis of materials as they flow through the production line. These sensors can measure everything from blend uniformity and moisture content to the chemical composition of an active pharmaceutical ingredient. Because these measurements are taken in real-time, any deviation from the desired specification can be detected and corrected immediately. This immediate feedback loop is essential for maintaining process stability and ensuring that every unit produced meets the required standards, thereby eliminating the “black box” nature of traditional manufacturing.
Implementation of Real Time Release Testing (RTRT)
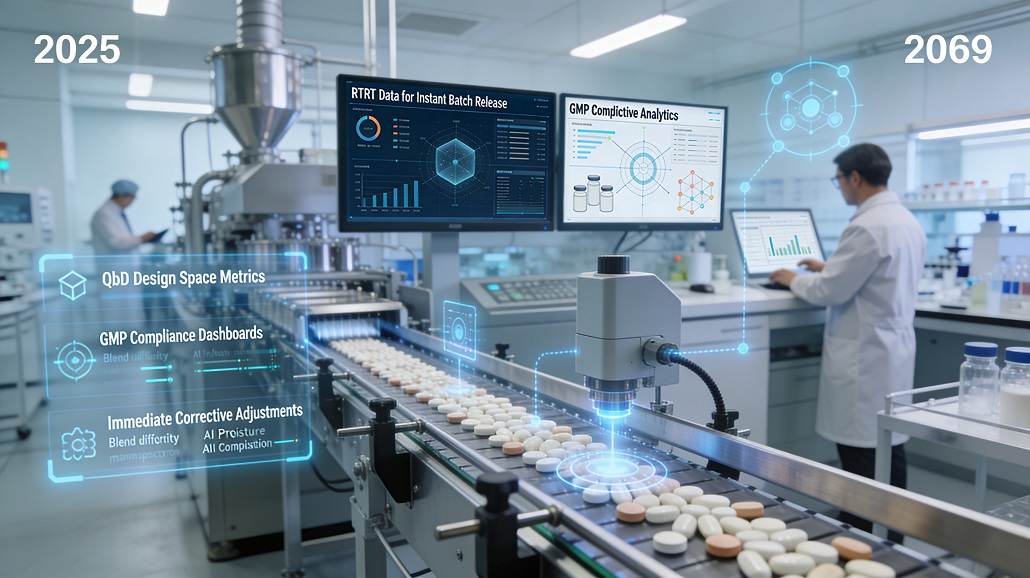
One of the most significant milestones enabled by process analytical technology in pharma is the transition toward Real Time Release Testing (RTRT). In a traditional manufacturing environment, products are held in quarantine for days or even weeks while laboratory tests are conducted to confirm their quality. With RTRT, the data collected by PAT sensors during the manufacturing process provides the evidence necessary to release the product immediately after production is complete. This drastically reduces inventory hold times, improves supply chain agility, and lowers the overall cost of goods. Regulatory bodies have become increasingly supportive of RTRT, recognizing that a well-controlled process monitored by PAT provides a higher level of quality assurance than a single test performed on a finished tablet.
Enhancing GMP Compliance and Regulatory Transparency
As the industry moves toward more complex biological therapies, maintaining GMP compliance becomes increasingly difficult. The use of process analytical technology in pharma provides a robust framework for meeting these regulatory demands. By generating a continuous stream of data, PAT systems create an unalterable digital record of the manufacturing process. This level of transparency is invaluable during regulatory inspections, as it provides inspectors with a clear and detailed view of how quality was managed for every batch. Furthermore, the ability to demonstrate a deep scientific understanding of the process through PAT data can lead to more flexible regulatory oversight, as agencies are more likely to trust manufacturers who can prove they have total control over their operations.
Integration with Pharma Quality Systems
For process analytical technology in pharma to be truly effective, it must be integrated into the broader pharma quality systems of the organization. This involves more than just installing sensors; it requires a cultural shift where data is used to drive continuous improvement. By analyzing the vast amounts of information generated by PAT tools, quality teams can identify subtle trends that may indicate a looming process failure or an opportunity for optimization. This predictive capability allows manufacturers to address issues before they impact product quality, moving from a reactive mode of operation to a proactive one. The integration of PAT data into the quality management system ensures that the entire organization is aligned around the goal of data-driven excellence.
Overcoming the Challenges of Technical Implementation
While the benefits are clear, the technical implementation of process analytical technology in pharma is not without its challenges. It requires a significant upfront investment in specialized sensors, software, and data management infrastructure. Furthermore, there is a substantial need for personnel who possess a unique blend of skills in chemistry, engineering, and data science. Developing the models needed to interpret spectroscopic data is a complex task that requires rigorous validation to ensure accuracy and reliability. Many companies are overcoming these hurdles by partnering with technology providers and academic institutions to build the necessary expertise and to develop standardized protocols for PAT implementation across their global manufacturing networks.
The Future of PAT and Autonomous Manufacturing
Looking ahead, the role of process analytical technology in pharma will only grow as the industry moves toward fully autonomous manufacturing. In this vision, AI-driven control loops will utilize PAT data to make real-time adjustments to the production line with zero human intervention. This will be particularly important for the production of personalized medicines, where the manufacturing process must be adapted for every individual patient. The ability of PAT to provide a high-resolution view of the process in real-time is the “nervous system” that will make this level of automation possible. As these technologies continue to mature, they will redefine the boundaries of what is possible in drug production, leading to a safer, more efficient, and more responsive global healthcare system.
Conclusion and Strategic Summary
In conclusion, process analytical technology in pharma is a transformative force that is driving the next wave of innovation in drug production. By enabling real-time monitoring and fostering a culture of Quality by Design, PAT is helping manufacturers achieve higher levels of precision, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. The shift toward Real Time Release Testing and the integration of PAT with smart quality systems are setting new benchmarks for the industry. While the journey toward full implementation requires a commitment to innovation and a significant investment in talent and technology, the rewards are profound. As we move into an era of increasingly complex and personalized therapies, PAT will remain the cornerstone of a data-driven manufacturing landscape that prioritizes the safety and health of patients above all else.