The global pharmaceutical industry is standing at the precipice of a transformative era where the boundaries between biological research and industrial execution are blurring. As we approach 2026, the reliance on advanced pharma manufacturing technologies has transitioned from a competitive advantage to a fundamental operational requirement. The shift is characterized by a move away from the traditional, rigid batch-processing models that have dominated the sector for decades, toward a more fluid, data-rich environment that prioritizes speed, accuracy, and uncompromising quality. This evolution is necessitated by the rise of personalized medicine, the complexity of novel biologics, and a regulatory environment that increasingly demands granular transparency throughout the product lifecycle.
The Architectural Foundation of the Smart Pharma Factory
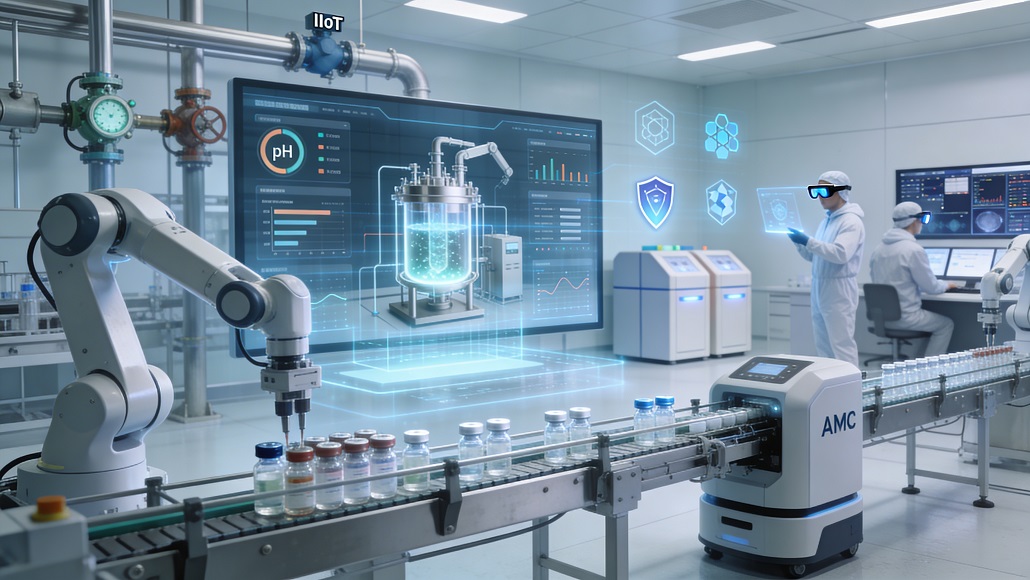
A central element of this future is the realization of the smart pharma factory. These next-generation facilities are built on a foundation of ubiquitous connectivity, where every sensor, valve, and robotic arm communicates within a unified digital architecture. Unlike the siloed systems of the past, the smart factory utilizes the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to create a comprehensive view of the manufacturing floor. This level of integration allows for the collection of massive datasets that were previously inaccessible, providing the raw material for advanced analytics engines. By 2026, the most successful manufacturers will be those who have moved beyond simple data collection and have mastered the art of extracting actionable intelligence in real-time, allowing them to optimize throughput while minimizing energy consumption and resource waste.
The Role and Impact of Digital Twins in Pharma
Within the sophisticated framework of the smart factory, the deployment of digital twins in pharma has become a cornerstone of process optimization. A digital twin is essentially a high-fidelity virtual model of a physical asset, whether that be a single bioreactor or an entire end-to-end production line. By mirroring the physical world in a digital space, manufacturers can simulate complex scenarios and predict outcomes with surgical precision. This capability is invaluable during the scale-up phase of drug development, as it allows engineers to identify potential bottlenecks or thermal deviations before a single drop of expensive material is processed. By 2026, digital twins will be used not just for planning, but for active control, with AI-driven models continuously adjusting physical parameters to maintain the “golden batch” conditions.
Advancing Real-Time Process Monitoring and Control
The efficacy of a digital twin is only as good as the data that feeds it, which has led to a significant surge in the sophistication of process automation. Traditional pharmaceutical manufacturing often relies on “post-mortem” quality testing, where samples are taken after a batch is completed and sent to a lab for analysis. This approach is inherently reactive and prone to significant waste if a deviation is discovered late in the process. Advanced pharma manufacturing technologies in 2026 prioritize real-time process monitoring through the use of advanced sensors and Process Analytical Technology (PAT). These tools allow for the constant measurement of critical quality attributes, such as pH levels, temperature gradients, and chemical concentrations, ensuring that the process remains within the strictly defined design space at all times.
Evolution toward Continuous Manufacturing Systems
While batch manufacturing will still have its place for certain applications, the trend toward continuous manufacturing is accelerating. This approach involves a constant flow of materials through the production line, eliminating the downtime associated with cleaning, setup, and intermediate storage. Continuous manufacturing offers a much smaller physical footprint, which is essential for facilities located in high-cost urban areas or those designed for rapid deployment. Furthermore, the inherent stability of continuous processes makes them ideal candidates for the application of advanced pharma manufacturing technologies, as the steady-state conditions allow for more precise control and more consistent product quality over long production runs.
Integration of Robotics and Cognitive Automation
To manage the complexities of continuous production and high-potency drug handling, the industry is increasingly turning to advanced robotics and cognitive automation. In 2026, robots are no longer just mechanical arms performing repetitive tasks; they are intelligent agents equipped with sophisticated vision systems and haptic feedback. These systems are used in sterile environments to eliminate the risk of human-introduced contamination, which remains one of the leading causes of batch failure. Beyond the cleanroom, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) navigate the facility floor, transporting raw materials and finished goods with minimal human intervention, thereby streamlining the internal supply chain and reducing the likelihood of logistical errors.
Maintaining Rigorous GMP Production Standards
As technology advances, the definition of GMP production is also evolving. Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA are increasingly supportive of manufacturers who utilize advanced pharma manufacturing technologies, provided they can demonstrate a high level of process understanding and control. The move toward “quality by design” means that compliance is no longer a hurdle at the end of the process but is integrated into the very fabric of the manufacturing system. By 2026, the use of blockchain for end-to-end traceability and electronic batch records (EBRs) will be the industry standard, providing an unalterable audit trail that ensures data integrity and simplifies the regulatory reporting process. This digital transparency is essential for building public trust, particularly as therapies become more complex and specialized.
The Influence of AI-Driven Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence is the cognitive layer that binds all these advanced pharma manufacturing technologies together. By 2026, AI-driven predictive analytics will be the standard tool for managing facility maintenance and production scheduling. These algorithms can analyze vibration patterns in motors, pressure fluctuations in filters, and heat signatures in electronic components to predict when a part is likely to fail. This shift from reactive to predictive maintenance drastically reduces unplanned downtime, which can cost manufacturers millions of dollars in lost productivity. Furthermore, AI is being used to optimize the yield of complex biological processes, where small changes in environmental conditions can have a massive impact on the final output.
Enhancing Cybersecurity for Interconnected Operations
With the benefits of connectivity comes the significant challenge of cybersecurity. As pharmaceutical facilities become more reliant on cloud-based analytics and remote monitoring, they become more vulnerable to cyber threats. Protecting the intellectual property of drug formulations and ensuring the integrity of manufacturing data is a critical concern for leadership in 2026. This has led to the development of robust cybersecurity frameworks tailored specifically for the pharmaceutical sector, utilizing advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and zero-trust architectures. Ensuring that the digital infrastructure is as secure as the physical facility is a prerequisite for any organization looking to implement advanced pharma manufacturing technologies at scale.
Strategic Investment in Human Capital and Talent
Despite the high level of automation, the future of pharma manufacturing is not without humans; rather, the role of the human worker is being elevated. The industry is facing a significant skills gap as the demand for professionals who understand both biology and data science increases. By 2026, successful organizations will be those that have invested heavily in upskilling their workforce to operate within a Pharma 4.0 environment. This includes training technicians to use augmented reality (AR) for equipment maintenance and providing engineers with the tools to manage complex AI models. The human element remains the ultimate arbiter of ethical decisions and creative problem-solving, ensuring that technology serves the ultimate goal of patient health.
The Path toward Personalized and Distributed Manufacturing
The long-term vision for advanced pharma manufacturing technologies includes the move toward personalized medicine and distributed manufacturing. This involves producing small, highly specialized batches of drugs close to the point of care, rather than in a few massive global hubs. Modular manufacturing units, equipped with the latest automation and digital twin capabilities, can be deployed in hospitals or regional clinics to produce tailor-made therapies for individual patients. This approach reduces the logistical challenges associated with cold-chain management and ensures that patients receive the most effective treatments in the shortest possible time.
Conclusion and Future Perspective
As we look toward 2026, it is clear that the integration of advanced pharma manufacturing technologies is redefining the potential of the pharmaceutical industry. The journey toward the smart pharma factory is marked by a commitment to data integrity, process efficiency, and patient safety. While the transition requires significant capital investment and a cultural shift within organizations, the benefits of higher yields, lower costs, and faster access to life-saving medicines are undeniable. The future of medicine is being built today on a foundation of intelligent automation and digital precision, ensuring that the next generation of therapies can be delivered to those who need them most with greater reliability than ever before.