The pharmaceutical industry is currently at the forefront of a technological revolution that is fundamentally altering how medicines are developed and produced. This movement, characterized by the rise of smart pharma plants and Industry 4.0, represents a shift toward a fully interconnected and intelligent manufacturing ecosystem. In these modern facilities, the traditional boundaries between the physical and digital worlds are blurring, creating a dynamic environment where data flows seamlessly between equipment, personnel, and global supply chains. As we look toward 2026, the integration of these advanced technologies is no longer an optional upgrade but a strategic imperative for organizations that wish to remain competitive in an increasingly complex and fast-paced healthcare market.
The Architecture of the Connected Pharma Factory
At the heart of any smart factory is a robust digital architecture that enables ubiquitous connectivity. Smart pharma plants and Industry 4.0 rely on the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to gather a constant stream of data from every corner of the production floor. Thousands of IoT sensors monitor everything from the vibration of a centrifugal pump to the precise humidity levels in a packaging room. This high-resolution data collection provides manufacturers with unprecedented visibility into their operations, allowing them to identify inefficiencies that were previously invisible. By creating a digital twin a virtual replica of the physical facility operators can simulate production scenarios and optimize workflows in a risk-free digital space before implementing changes in the real world.
Leveraging AI and Advanced Data Analytics
The true power of smart pharma plants and Industry 4.0 lies not just in the collection of data, but in its analysis. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are used to process the massive datasets generated by IIoT sensors, uncovering patterns and insights that human operators could never detect. These AI-driven systems are used to optimize everything from energy consumption to drug yields. In the laboratory, they accelerate drug discovery by predicting how different molecules will interact, while on the production line, they ensure that every batch is manufactured under the “golden batch” conditions. This move toward data-driven decision-making is essential for managing the complexity of modern biologics and for ensuring that product quality remains consistent across global manufacturing networks.
Implementation of Predictive Maintenance Strategies
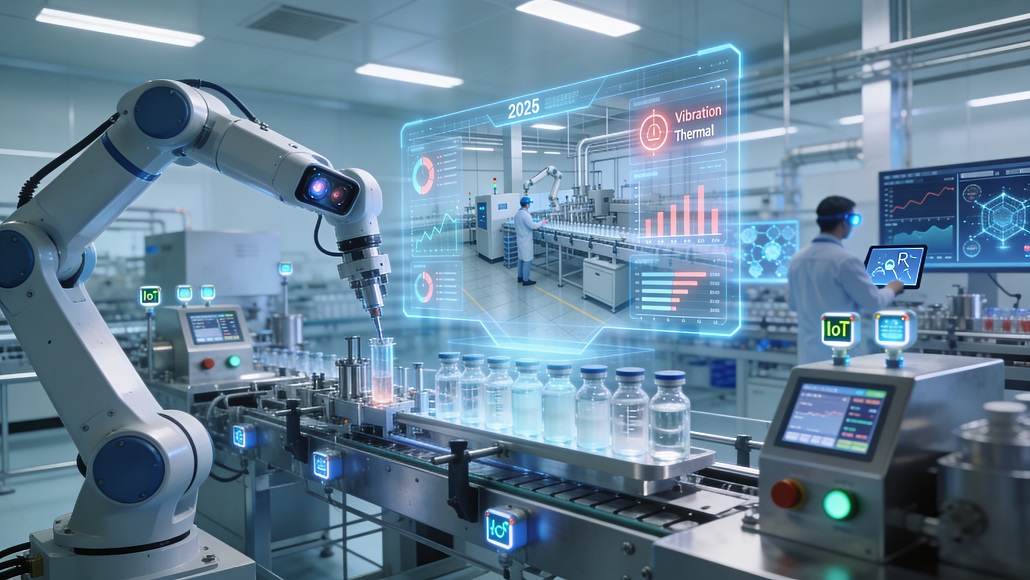
One of the most immediate benefits of adopting the principles of smart pharma plants and Industry 4.0 is the transition from reactive to predictive maintenance. In a traditional facility, equipment is often repaired only after it has failed, leading to costly unplanned downtime and potential batch loss. In a smart plant, AI algorithms analyze real-time data from vibration and thermal sensors to identify the early warning signs of equipment wear. This allows maintenance teams to intervene at the most opportune time, replacing a failing component during a scheduled break rather than waiting for a catastrophic failure. This proactive approach not only extends the life of critical assets but also ensures that production schedules remain on track, significantly improving the overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) of the facility.
Robotics and Automation in Sterile Environments
The use of advanced robotics is a defining feature of smart pharma plants and Industry 4.0. In the highly sensitive environments required for pharmaceutical production, human intervention is often the primary source of contamination. By automating repetitive and high-risk tasks, such as fill-finish operations and the handling of hazardous chemicals, companies can significantly enhance safety and compliance. Modern robotic systems are equipped with sophisticated vision and haptic sensors, allowing them to perform delicate tasks with a level of precision and consistency that exceeds human capability. These robots are also increasingly collaborative, designed to work alongside human operators to improve productivity while maintaining the highest standards of safety and sterility.
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience through Connectivity
The impact of smart pharma plants and Industry 4.0 extends far beyond the walls of the manufacturing facility. By connecting the production floor with the broader supply chain, companies can create a more resilient and responsive operation. Real-time data sharing with suppliers and logistics partners allows for a more accurate understanding of material needs and shipping schedules. This connectivity is particularly important for managing the complex cold-chain requirements of many modern vaccines and cell therapies. Technologies like blockchain are being used to provide end-to-end traceability, ensuring the authenticity of medications and helping to combat the global problem of counterfeit drugs. A smart, connected supply chain is a fundamental requirement for delivering the right medicine to the right patient at the right time.
Overcoming the Challenges of Digital Integration
While the vision of the smart factory is compelling, the path to implementation is fraught with challenges. Many pharmaceutical companies are burdened by legacy IT and OT (operational technology) systems that were never designed to be interconnected. Integrating these older assets with modern digital platforms requires a significant investment in both technology and talent. Furthermore, the increased connectivity of smart pharma plants and Industry 4.0 creates new cybersecurity risks that must be addressed. Protecting sensitive intellectual property and ensuring the integrity of production data is a top priority for leadership. Successful organizations are those that take a holistic approach, investing in robust cybersecurity frameworks alongside their digital transformation initiatives to ensure that their operations remain secure and resilient.
The Human Element in the Smart Factory Era
Despite the high level of automation, the role of the human worker in smart pharma plants and Industry 4.0 is becoming more important, not less. The transition to a digital factory requires a workforce with a new set of skills, including data science, automation engineering, and digital literacy. Organizations must invest heavily in upskilling and reskilling programs to ensure that their teams are prepared to operate in this new environment. Technologies like augmented reality (AR) are being used to provide technicians with real-time guidance during maintenance tasks, while virtual reality (VR) is transforming how personnel are trained for complex procedures. By empowering workers with digital tools, companies can foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement that is essential for long-term success.
Conclusion and Strategic Summary
In conclusion, the emergence of smart pharma plants and Industry 4.0 is a transformative development that is redefining the possibilities of drug production. By leveraging the power of IoT, AI, and robotics, manufacturers are achieving unprecedented levels of efficiency, quality, and resilience. The move toward predictive maintenance and connected supply chains is setting new standards for operational excellence. While the journey toward full digitalization is complex and requires significant investment, the benefits for patients and the industry are undeniable. As we move into an era of increasingly personalized and complex therapies, the smart factory will be the cornerstone of a data-driven manufacturing landscape that is capable of meeting the global health challenges of the 21st century.