The Future of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients in Global Supply Chains
Globalization has fundamentally transformed the ways in which pharmaceutical companies source and manufacture active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), ushering in both opportunities and challenges in an increasingly interconnected world. Over the past two decades, the API landscape has shifted from localized production hubs to a sprawling global network, with major manufacturing centers emerging in Asia, Eastern Europe, and Latin America.
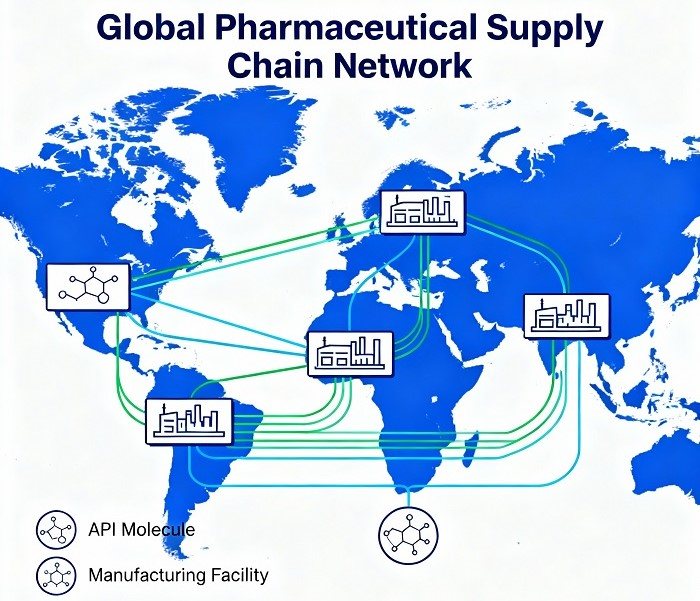
The Rise of Global API Hubs
During the early 2000s, India and China rapidly ascended as dominant API manufacturing centers due to lower production costs and favorable government incentives. By leveraging economies of scale, these hubs reshaped the API supply chain, enabling multinational pharmaceutical corporations to optimize expenses while scaling production volumes. However, this concentration also introduced geopolitical risks and vulnerabilities, as global events or regional disruptions could ripple across the supply network.
Regulatory Pressures and Quality Assurance
Heightened scrutiny from regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA has reshaped API sourcing strategies. In recent years, regulators have intensified inspections and compliance requirements, prompting pharmaceutical firms to diversify sourcing and implement stringent quality measures. As a result, companies have established multi-tiered supplier qualification processes, ensuring every link within the active pharmaceutical ingredients supply chain adheres to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Supply Chain Resilience and Reshoring Initiatives
The aftermath of global health crises and geopolitical tensions has spurred discussions around reshoring critical API production. Several governments have introduced incentives and subsidies to encourage domestic manufacturing, fostering greater supply chain resilience. However, reshoring presents trade-offs: while it reduces dependency on foreign suppliers, higher operating costs and scale limitations can impact affordability and availability.
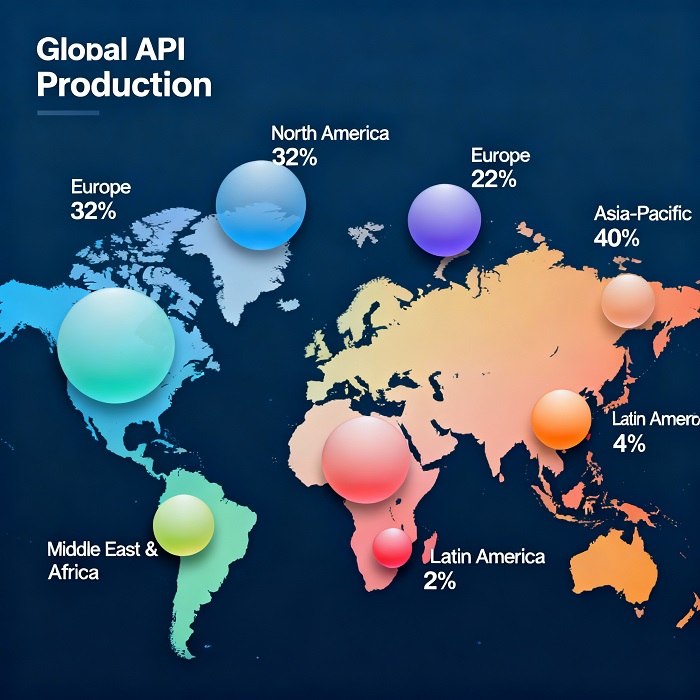
Emerging Trends in API Manufacturing
As demand for complex biologics and specialty APIs grows, manufacturers are adopting advanced technologies to enhance efficiency and sustainability. Continuous manufacturing platforms, process intensification, and digital twins are redefining traditional batch processes. This evolution not only streamlines production but also fortifies quality control, enabling real-time monitoring within the API manufacturing workflow.
Strategic Supplier Partnerships
To navigate regulatory complexities and market volatility, pharmaceutical companies are forging strategic alliances with key API suppliers. These partnerships often encompass co-investment in capacity expansion, joint quality audits, and collaborative R&D for novel molecules. Such synergies bolster innovation while reinforcing supply chain security.
Conclusion
The future of active pharmaceutical ingredients supply chain management hinges on balancing globalization’s efficiencies with proactive risk mitigation. By diversifying sourcing, embracing technological advancements, and strengthening regulatory adherence, the pharmaceutical industry can ensure consistent, high-quality API availability. As reshoring initiatives and strategic collaborations gain momentum, the API ecosystem will continue evolving—paving the way for resilient, agile supply networks in the years ahead.